OFDM is an attractive modulation scheme used in broadband wireless systems that encounter large delay spreads. OFDM avoids temporal equalization altogether, using a cyclic prefix technique with a small penalty in channel capacity.
Where Line-of-Sight (LoS) cannot be achieved, there is likely to be significant multipath dispersion, which could limit the maximum data rate. Technologies like OFDM are probably best placed to overcome these, allowing nearly arbitrary data rates on dispersive channels.
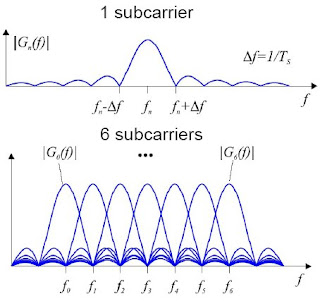
OFDM signals have a large peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR) due to the superposition of all subcarrier signals. Therefore, in each Transmitter the power amplifier will limit the OFDM signal by its maximal output power. This also disturbs the orthogonality between subcarriers, leading to both intercarrier and out-of-band interferences, which is unacceptable.



Wow, good explain.
ReplyDeleteThanks