Call Setup
Different procedures are necessary depending on the initiating and terminating party:
- Mobile Originating Call MOC: Call setup, which are initiated by an MS
- Mobile Terminating Call MTC: Call setup, where an MS is the called party
- Mobile Mobile Call MMC: Call setup between two mobile subscribers; MMC thus consists of the execution of a MOC and a MTC one after the other.
- Mobile Internal Call MIC: a special case of MMC; both MSs are in the same MSC area, possibly even in the same cell.
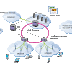
Mobile Originating Call MOC
1. Channel Request: The MS requests for the allocation of a dedicated signaling channel to perform the call setup.
2. After allocation of a signaling channel the request for MOC call setup, included the TMSI (IMSI) and the last LAI, is forwarded to the VLR
3. The VLR requests the AC via HLR for Triples (if necessary).
4. The VLR initiates Authentication, Cipher start, IMEI check (optional) and TMSI Re-allocation (optional).
5. If all this procedures have been successful, MS sends the Setup information (number of requested subscriber and detailed service description) to the MSC.
6. The MSC requests the VLR to check from the subscriber data whether the requested service an number can be handled (or if there are restrictions which do not allow further proceeding of the call setup)
7. If the VLR indicates that the call should be proceeded, the MSC commands the BSC to assign a Traffic Channel (i.e. resources for speech data transmission) to the MS
8. The BSC assigns a Traffic Channel TCH to the MS
9. The MSC sets up the connection to requested number (called party).
Remark: This MOC as well as the MTC described in the following describes only the principles of an MOC / MTC, not the detailed signaling flow.





No comments:
Post a Comment