The SIM card can be protected against unauthorised access with a four- to eight-digit Personal Identification Number ( PIN). After switching on the mobile phone, the subscriber identifies himself to the card by entering this PIN. If an unauthorised person gains possession of a SIM card, he cannot use it without also knowing the PIN. To prevent improper use of the SIM card, the PIN should therefore be kept in safe place.
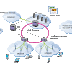
The subscriber identifies himself to the network provider on registering by means of the SIM card and the cryptographic algorithms held on it. Authentication is effected with the aid of an authentication key which is known only to the network provider in the AUC and the subscriber on the SIM card.
Normally the data is only transmitted encrypted on the radio link between the mobile phone and the base station. Encryption is not used on any of the other transmission paths, either in the
GSM network or in the landline domain. For operational reasons, even on the radio link it is possible for the encryption procedure not to be applied, in which case data will then be transmitted unencrypted. Depending on the statutory requirements, in some countries encryption of transmissions can be completely disabled or individual security parameters can be weaker.
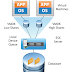
We using SRES fot that as :
SRES:= A3(RAND,Ki) . Signal response (SRES)
Thursday, April 7, 2011
Authentication in GSM
Tags
# AUC
# Authentication
# GSM
# SRES

About DISASTERS NEWS
Mahmoud Elgindy, 31 YO. Communications engineer and working as Network Engineer. My intersts are focus on Security and Cyber saftey. My hobbies are Programming and Big Data analysis.
SRES
Labels:
AUC,
Authentication,
GSM,
SRES
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)




No comments:
Post a Comment