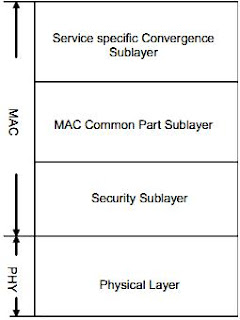
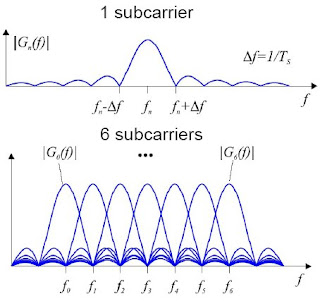
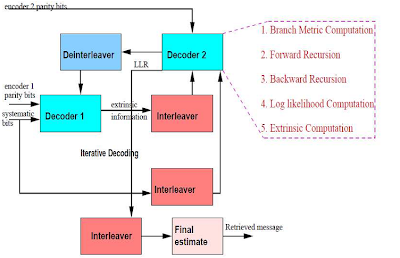
• Designing a cellular system - particularly one that incorporates both Macrocellular and Microcellular networks is a delicate balancing exercise.
• The goal is to achieve optimum use of resources and maximum revenue potential whilst maintaining a high level of system quality.
• Full consideration must also be given to cost and spectrum allocation limitations.
• A properly planned system should allow capacity to be added economically when traffic demand increases.
• As every urban environment is different, so is every macrocell and microcell network. Hence informed and accurate planning is essential in order to ensure that the system will provide both the increased capacity and the improvement in network quality where required,
especially when deploying Microcellular systems.
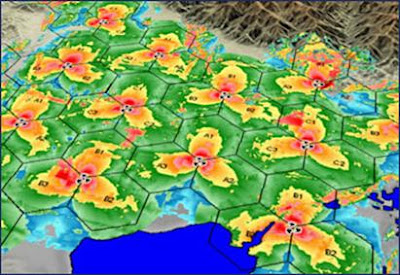
• RF planning plays a critical role in the Cellular design process.
• By doing a proper RF Planning by keeping the future growth plan in mind we can reduce a lot of problems that we may encounter in the future and also reduce substantially the cost of optimization.
• On the other hand a poorly planned network not only leads to many Network problems , it also increases the optimization costs and still may not ensure the desired quality.
• The goal is to achieve optimum use of resources and maximum revenue potential whilst maintaining a high level of system quality.
• Full consideration must also be given to cost and spectrum allocation limitations.
• A properly planned system should allow capacity to be added economically when traffic demand increases.
• As every urban environment is different, so is every macrocell and microcell network. Hence informed and accurate planning is essential in order to ensure that the system will provide both the increased capacity and the improvement in network quality where required,
especially when deploying Microcellular systems.

• RF planning plays a critical role in the Cellular design process.
• By doing a proper RF Planning by keeping the future growth plan in mind we can reduce a lot of problems that we may encounter in the future and also reduce substantially the cost of optimization.
• On the other hand a poorly planned network not only leads to many Network problems , it also increases the optimization costs and still may not ensure the desired quality.